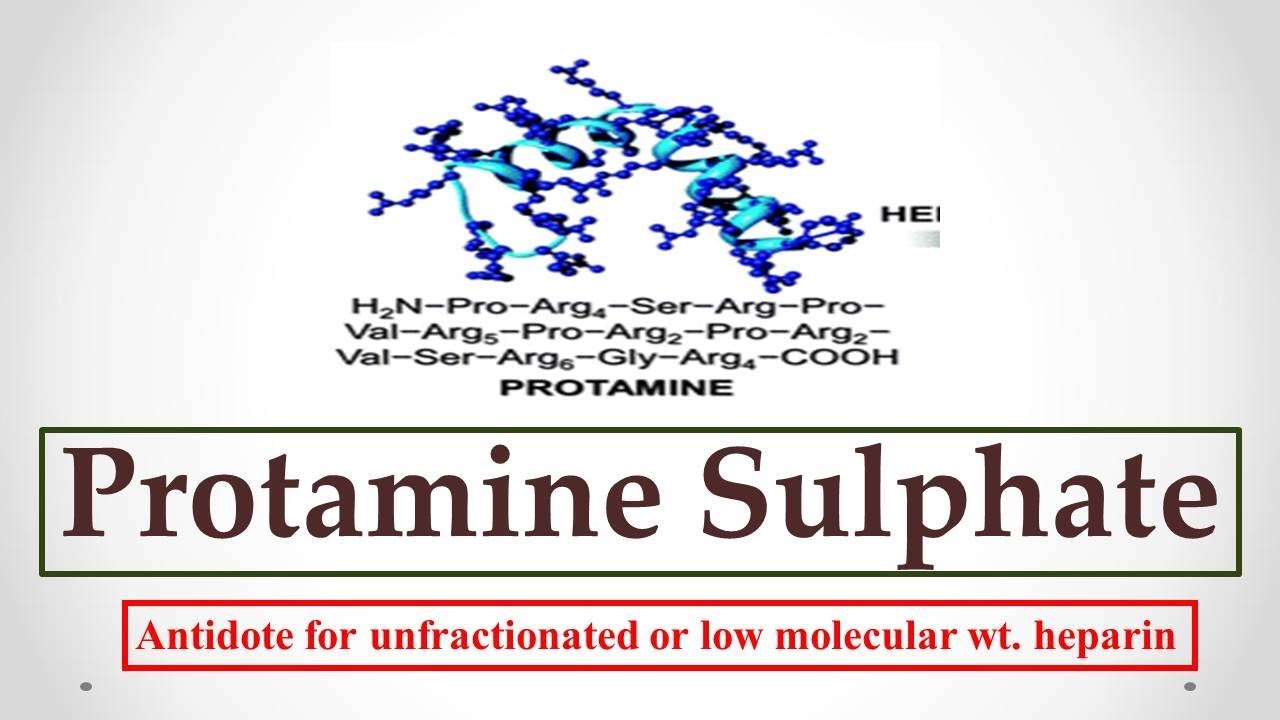
Antedote For Heparin. Protamine sulphate is a polypeptide originally derived from salmon sperm which binds to unfractionated heparin and. It is used when quick reversal of the action of heparin is needed as in case of bleeding or after an open heart surgery. When a bleeding complication occurs during therapy with heparin or vitamin k antagonists there is an option to give a specific antidote. Acetylsalicylic acid aspirin is used to decrease coagulation as a preventive measure for myocardial infarction.
Several new anticoagulants have been developed that are likely to have some risk of bleeding complications for which no specific antidotes are available. Acetylsalicylic acid aspirin is used to decrease coagulation as a preventive measure for myocardial infarction. Protamine sulphate is a polypeptide originally derived from salmon sperm which binds to unfractionated heparin and. Protamine sulfate a compound derived from purified fish sperm is the antidote for heparin. Low molecular weight protamine is under development. If immediate reversal is required protamine sulfate will result in neutralization of heparin.
The dose of protamine is based on the amount of heparin administered in the previous 2 hours using table 2.
Several new anticoagulants have been developed that are likely to have some risk of bleeding complications for which no specific antidotes are available. Table 2 protamine sulfate for immediate. The dose of protamine is based on the amount of heparin administered in the previous 2 hours using table 2. Several new anticoagulants have been developed that are likely to have some risk of bleeding complications for which no specific antidotes are available. Termination of the iv infusion generally will terminate the anticoagulant effect. Heparin antidote is protamine sulphate.