Blood Clot Prophylaxis. Ask your patients about any history in themselves or family of blood clotting or bleeding disorders. Many foods can either thin or thicken your blood depending on their key ingredients. Pharmacological dvt prophylaxis involves the administration of drugs like low molecular weight heparin to prevent clotting. Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis and screening for nonhospitalized patients with covid 19 anticoagulants and antiplatelet therapy should not be initiated for the prevention of venous thromboembolism vte or arterial thrombosis unless the patient has other indications for the therapy or is participating in a clinical trial aiii.

As a natural blood thinner garlic may also help prevent dvt. Recognize risk factors prior to orthopaedic surgery and plan accordingly for proper vte prophylaxis. A blood clot in the lungs is called a pulmonary embolism or pe. Anticoagulation practice has typically included at least prophylactic dosing for hospitalized covid 19 patients due to the excess clotting risk seen with the coronavirus. Drinking plenty of water is great considering that dehydration makes blood thicker. A blood clot in one of the large veins usually in a person s leg or arm is called a deep vein thrombosis or dvt.
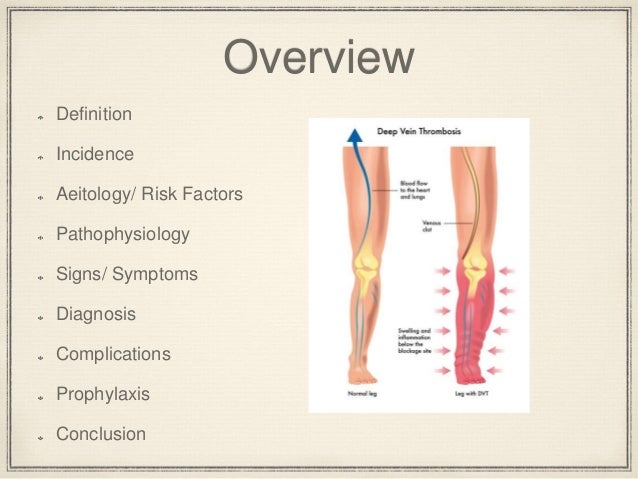
A blood clot in one of the large veins usually in a person s leg or arm is called a deep vein thrombosis or dvt.
As a natural blood thinner garlic may also help prevent dvt. Pharmacological dvt prophylaxis involves the administration of drugs like low molecular weight heparin to prevent clotting. The patient may take these drugs for varying amounts of time depending on the risks and the situation. Clarence crafoord is credited with the first use of thrombosis prophylaxis in the 1930s. Drinking plenty of water is great considering that dehydration makes blood thicker. Thrombosis prophylaxis is effective in preventing the formation of blood clots their lodging in the veins and their developing into thromboemboli that can travel through the circulatory system to cause blockage and subsequent tissue death in other organs.