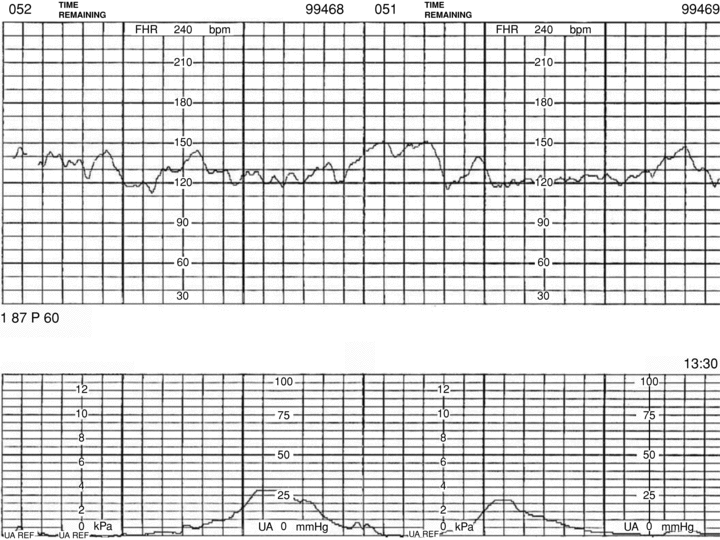
Fetal Heart Rate Accelerations. 11 a scalp ph less than 7 25 but greater than 7 20 is considered suspicious or borderline. Fetal heart rate accelerations accels during labor and delivery the heart rate of a fetus should remain steady but with the application of force during contractions may accelerate from the baseline rate. However the presence of accelerations are not serious and merely warn th. Fetal scalp sampling for ph is recommended if there is no acceleration with scalp stimulation.
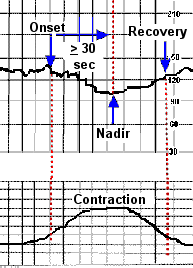
Acceleration of the fetal heart rate. The fetal heart rate fhr acceleration elicited by sound stimulus was defined as when it began within 60 s and continued 10 120 s after the stimulus. For example when your baby moves his heart rate should increase. A normal baseline fetal heart rate usually falls between 120 and 160 beats per minute. Fetal heart rate fhr accelerations that are accompanied by fetal movements are considered to be a good indication of fetal well being 2 nonstress testing based on the occurrence of fhr accelerations associated with fetal movement during a certain period gained unprecedented popularity among obstetricians and perinatalogists. Acceleration of the fetal heart rate during contractions was usually followed by deceleration and evidence is presented to show that it results from increased sympathetic drive and may be associated with fetal tissue hypoxia.
Acceleration of the fetal heart rate during contractions was usually followed by deceleration and evidence is presented to show that it results from increased sympathetic drive and may be associated with fetal tissue hypoxia.
The fetal heart rate fhr acceleration elicited by sound stimulus was defined as when it began within 60 s and continued 10 120 s after the stimulus. Moreover the amplitude of the fhr acceleration was defined as 10 bpm or more at 20 31 weeks gestational age and 15 bpm or more at 32 37 weeks gestational age. When the heart rate rises above 160 bpm it is referred to as tachycardia very rapid heart rate. Fetal scalp sampling for ph is recommended if there is no acceleration with scalp stimulation. Acceleration of the fetal heart rate during contractions was usually followed by deceleration and evidence is presented to show that it results from increased sympathetic drive and may be associated with fetal tissue hypoxia. Most commonly the nonstress test is considered reactive or normal if there are two or more fetal heart rate accelerations within a 20 minute period with or without fetal movement discernible by.