
G Tube Infection. Learn about how to prevent gastrointestinal and skin infection around the feeding tube site. Infection is uncommon in children with healthy immune systems. The reported rates of complications following percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy peg tube placement vary from 16 to 70 percent 1 5. Wash your hands every time you handle the tube site or formula and feeding supplies.
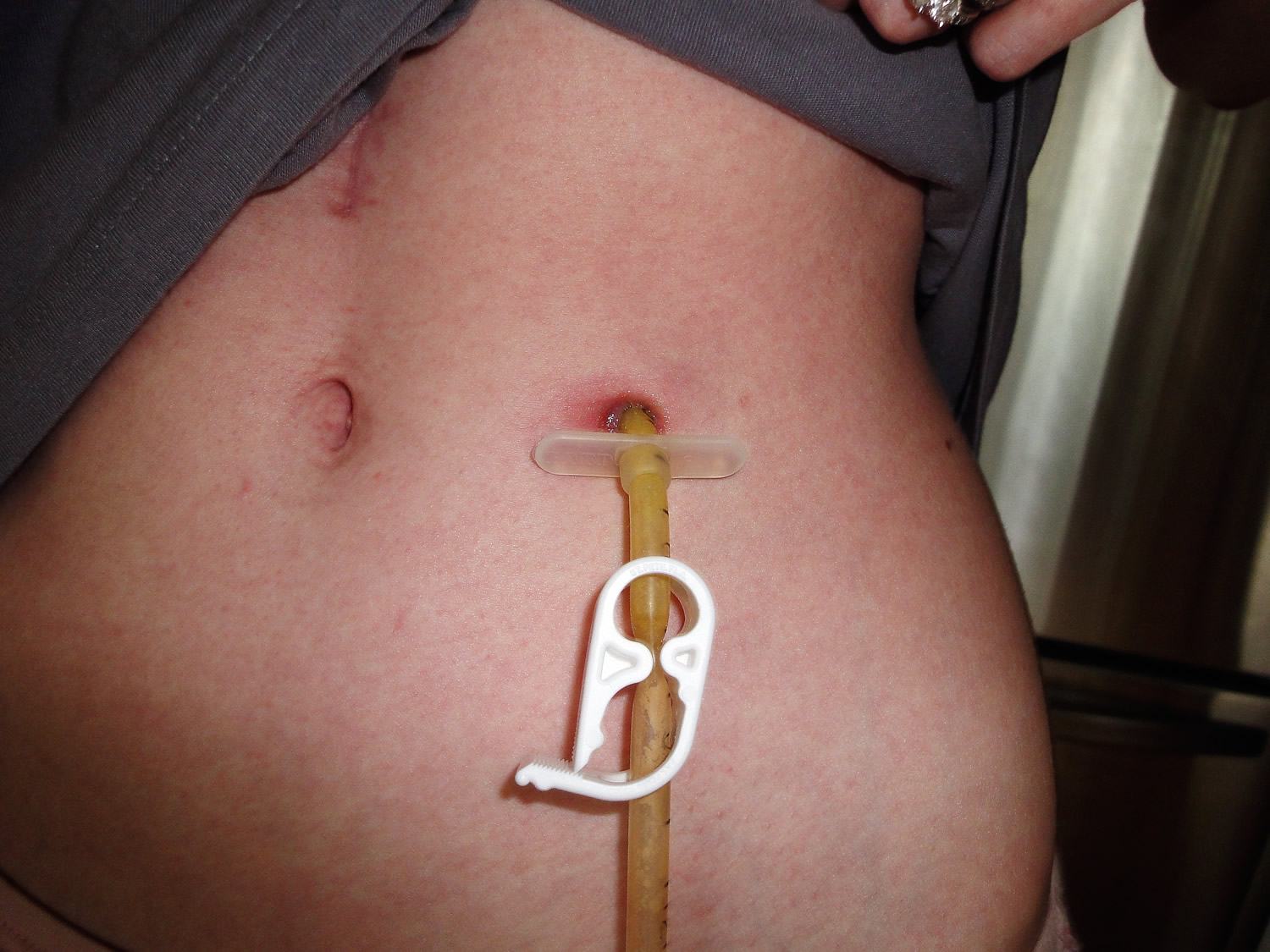
Under the skin flange use topical antifungal preparations eg clotrimazole or nystatin. The g tube does not need to be removed routinely unless there are signs of peritonitis necrotizing fasciitis or the infection does not respond to initial antibiotic treatment. Rarely the stoma or tube site may become infected. These tubes should only be inserted if they extend meaningful life in patients. Infection is uncommon in children with healthy immune systems. Weepy oozing or pus filled stoma.
Wash your hands every time you handle the tube site or formula and feeding supplies.
Infection is uncommon in children with healthy immune systems. G tube complication management infection. Prevent infection related to tube feeding with proper daily care. Angry red or red streaked stoma. Protocols are needed for the care of gastrosto. Use a new feeding bag daily or as instructed by your healthcare team.