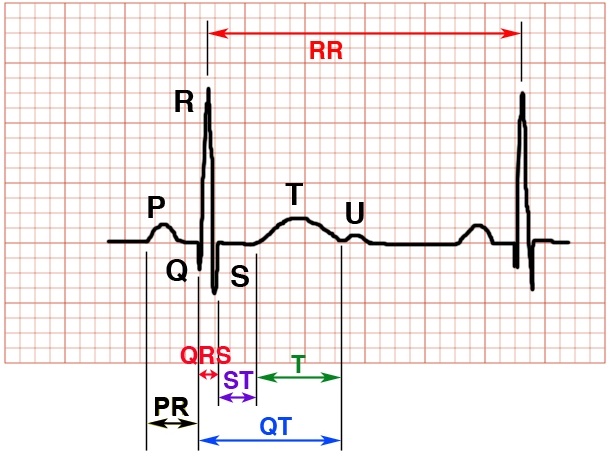
Measuring Ecg Strips. 1 0 1 electrocardiogram ecg 1 0 2 graphic recording of electrical potential generated due to transmission of depolarization wave or cardiac impulse through the heart and due to its spread into surrounding tissue and body surface. The second line should be exactly 30 large squares subsequent to the first line. Ecg paper is a grid where time is measured along the horizontal axis. Find the p wave on the ekg strip.
When our eyes are continuously exposed to the ekg strips we develop that skill of pinpointing the abnormalities at a much faster rate. Remember each box represents 0 04 seconds. Attain a 6 second ekg strip 30 large boxes and multiply the number of p waves in the six second strip by 10 to determine the number of atrial beats in one minute. P wave is the first short upward movement of the ecg tracing. Ecg paper is a grid where time is measured along the horizontal axis. 1 0 1 electrocardiogram ecg 1 0 2 graphic recording of electrical potential generated due to transmission of depolarization wave or cardiac impulse through the heart and due to its spread into surrounding tissue and body surface.
Each larger square is 5 mm in length and represents 0 2 seconds.
Determine where the pr interval is and to do this you start measuring at the beginning of the p wave until the beginning of the qrs complex. To determine the number of ventricular contraction multiply the number of r waves in the 6 second ekg strip by 10. So if you measure 2 boxes the measurement of the pr interval would be 0 08 seconds. If a patient s heart rhythm is irregular the first method of heart rate calculation doesn t work as the r r interval differs significantly throughout the ecg. Find the p wave on the ekg strip. 1 0 1 electrocardiogram ecg 1 0 2 graphic recording of electrical potential generated due to transmission of depolarization wave or cardiac impulse through the heart and due to its spread into surrounding tissue and body surface.