Sympathetic Storming After Traumatic Brain Injury. Boeve et al 1998. This article reviews the pathophysiology of sympathetic storming variations in signs and symptoms potential treatment options and education of families. Sympathetic storming after traumatic brain injury. The ongoing double blind randomised clinical trial decreasing adrenergic or sympathetic hyperactivity after traumatic brain injury dash after tbi is comparing combination therapy with propranolol and clonidine versus placebo in patients with severe tbi in the icu and results should provide some clarity about the efficacy of these drugs in controlling sympathetic hyperactivity in patients with psh in the icu setting.

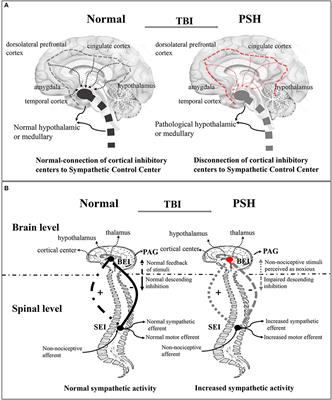
Sympathetic storming can occur within the first 24 hours after injury or up to weeks later 1 the precise mechanism for the increase in activity of the sympa thetic nervous system is unknown. Sympathetic storming after severe traumatic brain injury crit care nurse. Paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity psh has predominantly been described after traumatic brain injury tbi which is associated with hyperthermia hypertension tachycardia tachypnea. Russo o flaherty 2000. Author denise m lemke 1 affiliation 1 department of neurology. The sns controls your body s fight or flight response which occurs when your brain detects imminent danger.
The sns controls your body s fight or flight response which occurs when your brain detects imminent danger.
Sympathetic storming tends to be associated with lower neurological functional level and can be caused by injury or pressure created by tumors hydrocephalus or subarachnoid hemorrhage though it is most commonly seen in the tbi population baguley et al 1999. Sympathetic storming tends to be associated with lower neurological functional level and can be caused by injury or pressure created by tumors hydrocephalus or subarachnoid hemorrhage though it is most commonly seen in the tbi population baguley et al 1999. Following acute multiple trauma hypothalamic stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system and adrenal glands causes an increase in circulating corticoids and catecholamines or a stress response. Storming after brain injury refers to an excessive response of the sympathetic nervous system sns. This article reviews the pathophysiology of sympathetic storming variations in signs and symptoms potential treatment options and education of families. Paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity psh has predominantly been described after traumatic brain injury tbi which is associated with hyperthermia hypertension tachycardia tachypnea diaphoresis dystonia hypertonia or spasticity and even motor features such as extensor flexion posturing.