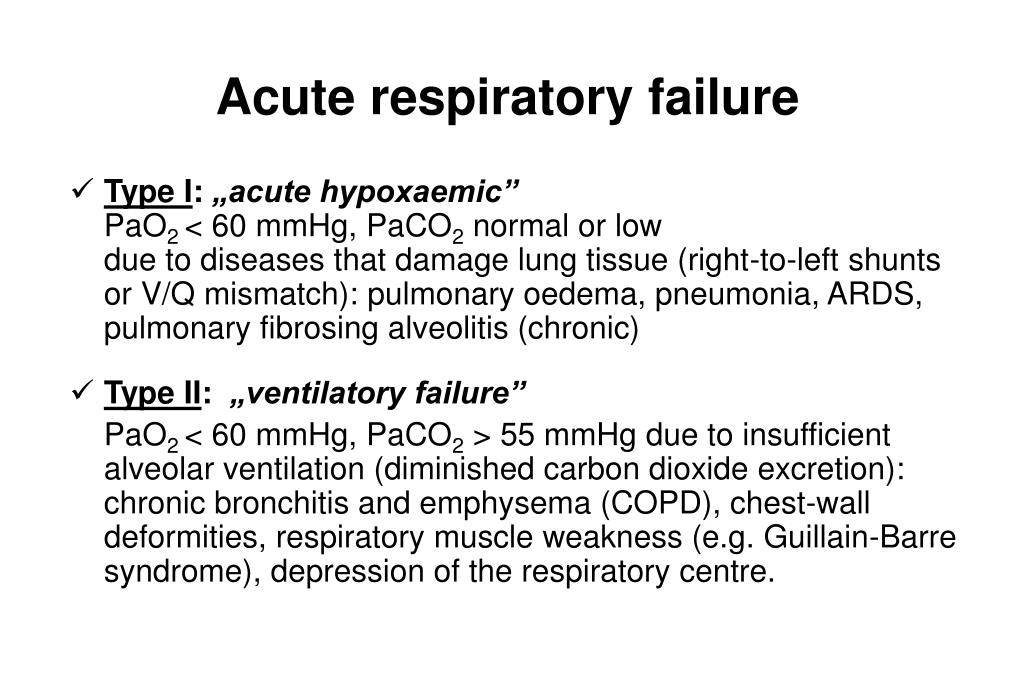
Type Respiratory Failure. Respiratory failure occurs due mainly either to lung failure resulting in hypoxaemia or pump failure resulting in alveolar hypoventilation and hypercapnia. Respiratory failure is classified as either type 1 or type 2 based on whether there is a high carbon dioxide level and can be either acute or chronic. It may or may not accompany hypercapnia a paco 2 higher than 50 mm hg decreased co 2 elimination. Normal physiology of respiration.
Type 1 hypoxemic respiratory failure has a pao2 60 mmhg with normal or subnormal paco2. Respiratory failure occurs due mainly either to lung failure resulting in hypoxaemia or pump failure resulting in alveolar hypoventilation and hypercapnia. Respiratory failure is divided into type i and type ii. Hypercapnic respiratory failure type ii is characterized by a. Type 2 respiratory failure hypercapnic. Types of acute respiratory failure the two types of acute and chronic respiratory failure are hypoxemic and hypercapnic.
Type ii respiratory failure involves low oxygen with high carbon dioxide.
Occurs when alveolar ventilation is insufficient to excrete the carbon dioxide being produced. In this type the gas exchange is impaired at the level of aveolo capillary membrane. Some examples of type i respiratory failure are cardiogenic or noncardiogenic pulmonary edema pneumonia and pulmonary hemorrhage. It may or may not accompany hypercapnia a paco 2 higher than 50 mm hg decreased co 2 elimination. Respiratory failure is classified according to blood gases abnormalities into type 1 and type 2. Statistics on respiratory failure types i and ii.